About
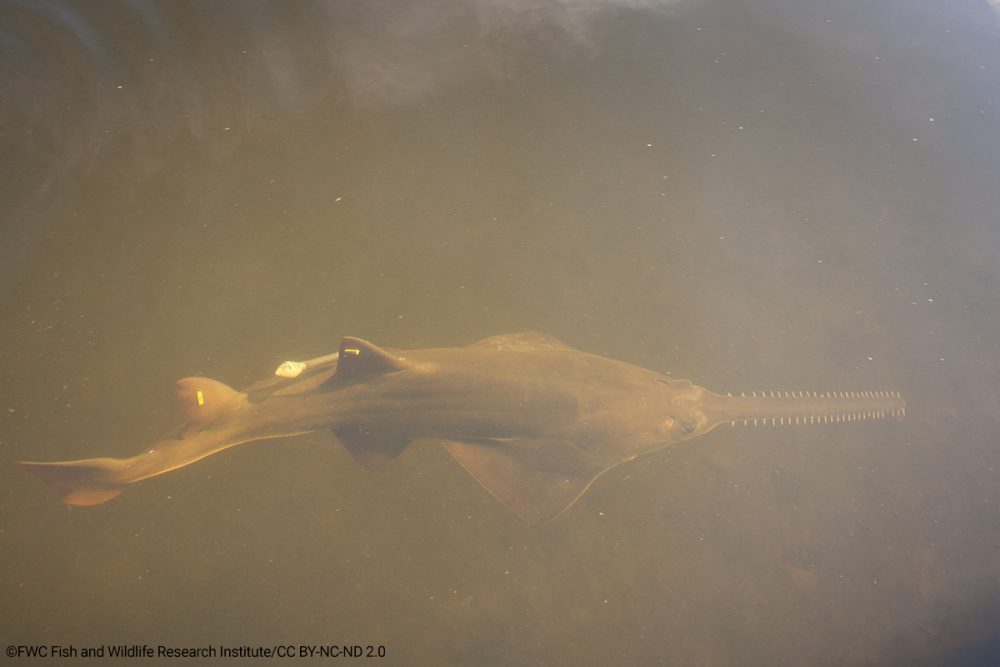
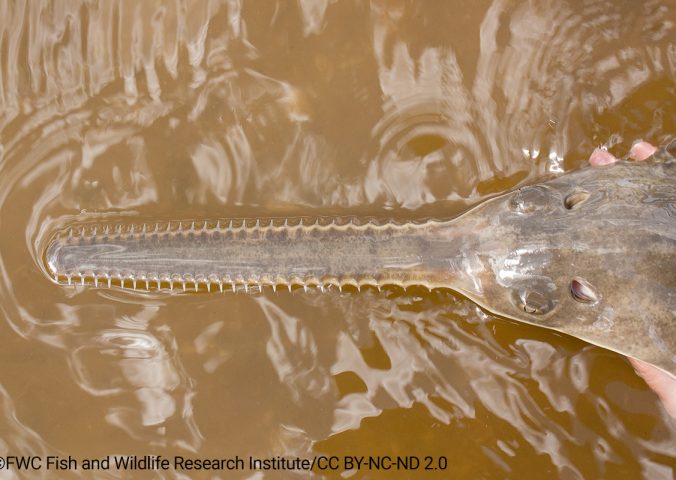
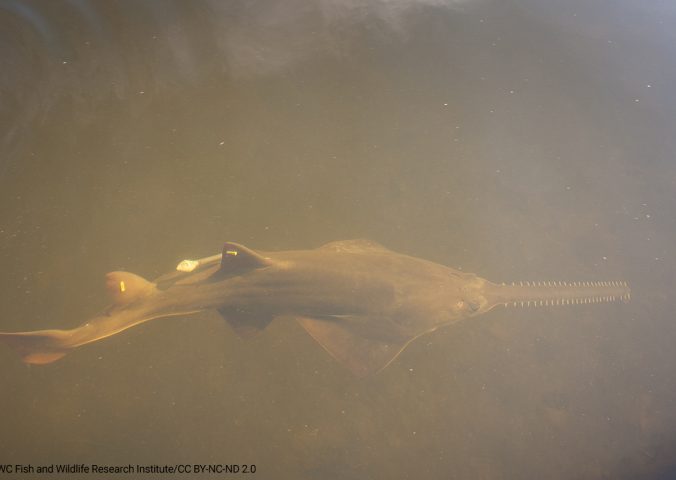
Sawfish are characterised by their large and unique saw-like rostra. The smalltooth sawfish has a narrower saw-like rostrum and is a smaller size than its relative the largetooth sawfish.
Historically, these rays were regularly encountered within the coastal waters of West Africa and the Americas, although overexploitation has resulted in a large reduction of their range, which is now limited to the South-eastern United States and small pockets of Central America. Most of the information on this species biology and ecology has been obtained from this sub-population.
Females have litters of approximately 20 pups.The smalltooth sawfish reproduce through yolk-sac viviparity, in which the embryos feed exclusively from the egg’s yolk inside the females, and the fully developed pups are born alive at approximately 60 cm long, after a one-year gestation period that occurs every two years. In South Florida, parturition (giving birth to live young) takes place between November and July, peaking in April and May. Juvenile growth rate has been found to be greater than previously thought, giving a good prognosis for the species recovery potential. Maturity is reached at around 270 cm and 360 cm.
Although it is thought that only between 1% and 5% of the US sub-population remains, it possesses high genetic diversity, 99% of which is estimated to be retained over the next century.
The smalltooth sawfish global population has decreased due to demand for their fins used in shark fin soup, their rostra used in traditional medicine, and their skin used to produce luxury leather; as well as the accelerated modification and degradation of its habitat. However, since the species became scarce, their biggest threat is accidental death from being caught in fishing nets, as well as long lines and hook and lines. This species is particularly susceptible to net-entangling because of their long-toothed rostra.
The IUCN Species Specialist Group consider conservation prioritise as, the protection of the species at national level, enforcement of the CITES ban, reduction in bycatch mortality, conservation of mangrove and other coastal tropical and subtropical habitats, and regional recovery plans.
- Order: Pristiformes
- Family: Pristidae
- Population: 200-500
- Trend: decreasing
- Size: Up to 550 cm (?)
- Weight: Up to 350kg
- Depth Range (m): up to 88 m, usually <10 m
EDGE Score
Distribution
Atlantic and South-West Indian Oceans, with numerous local extinctions resulting in fragmented subpopulations known to occur within tropical waters of the South-eastern United States, the Bahamas, Cuba, Honduras and Belize.
Habitat and Ecology
Smalltooth sawfish inhabit estuaries and shallow marine habitats, particularly mangrove forests and seagrass beds. Juveniles utilise brackish nursery habitats such as shallow stretches of water with preference for mangrove shorelines until maturity, when they move to coastal areas.
Juveniles’ local movements are very much influenced by salinity patterns in brackish waters and by mangrove presence and the species shows a degree of site fidelity which highlights the importance of managing these nursery areas.