EDGE Amphibians invites you to enter a world where toads give birth through the skin on their backs, legless caecilians burrow through the soil, and blind cave salamanders survive for a decade or more without food.
The amphibians were the original custodians of the land, being the vanguard of the terrestrial (or ground-dwelling) vertebrate invasion. Next time you look at a frog in your garden, consider that its ancient ancestors explored the land 140 million years before the dinosaurs. In fact, recent evidence suggests the most recent common ancestor of all amphibians roamed the earth over 315 million years ago. In this time, amphibians have diverged and evolved vastly different appearances and behaviours, from the 1.8-metre-long Chinese giant salamander to the worm-like Sagalla caecilian and the mouth brooding Chile Darwin frog, who carry their young in their vocal sac.

There are more than 7,650 species of amphibians currently known, and even more species are described each year. The vast majority of amphibians are frogs and toads (~6750 species), followed by salamanders (~710 species) and caecilians (~205 species). However, amphibians face unprecedented threats from habitat loss, climate change and disease and populations worldwide are disappearing.
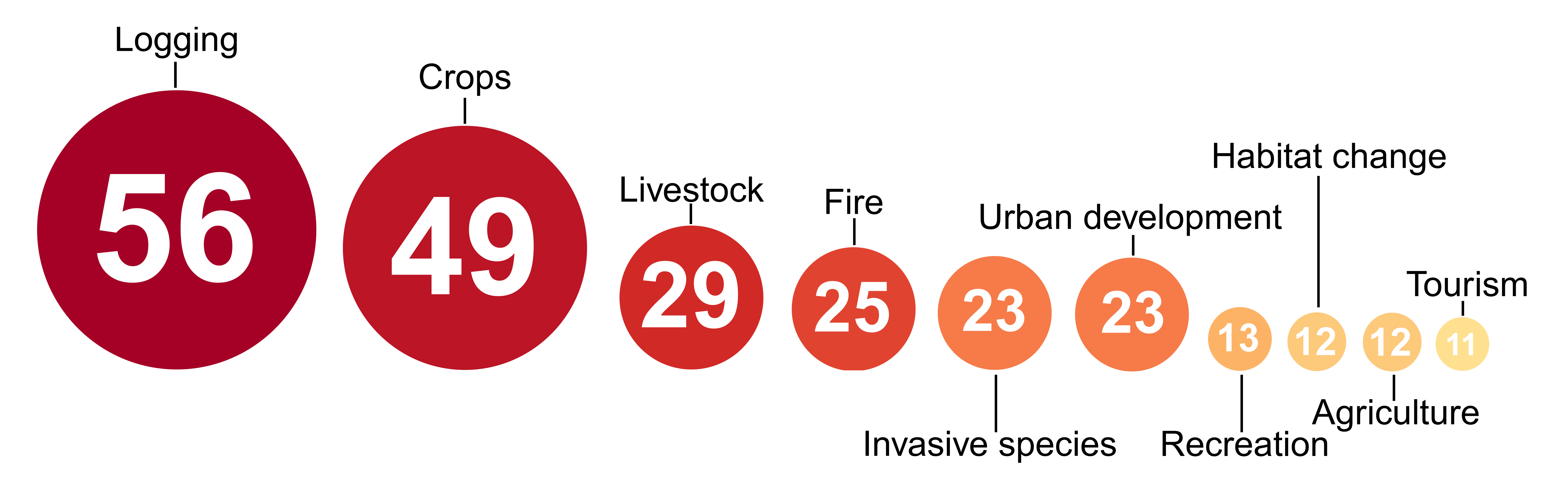
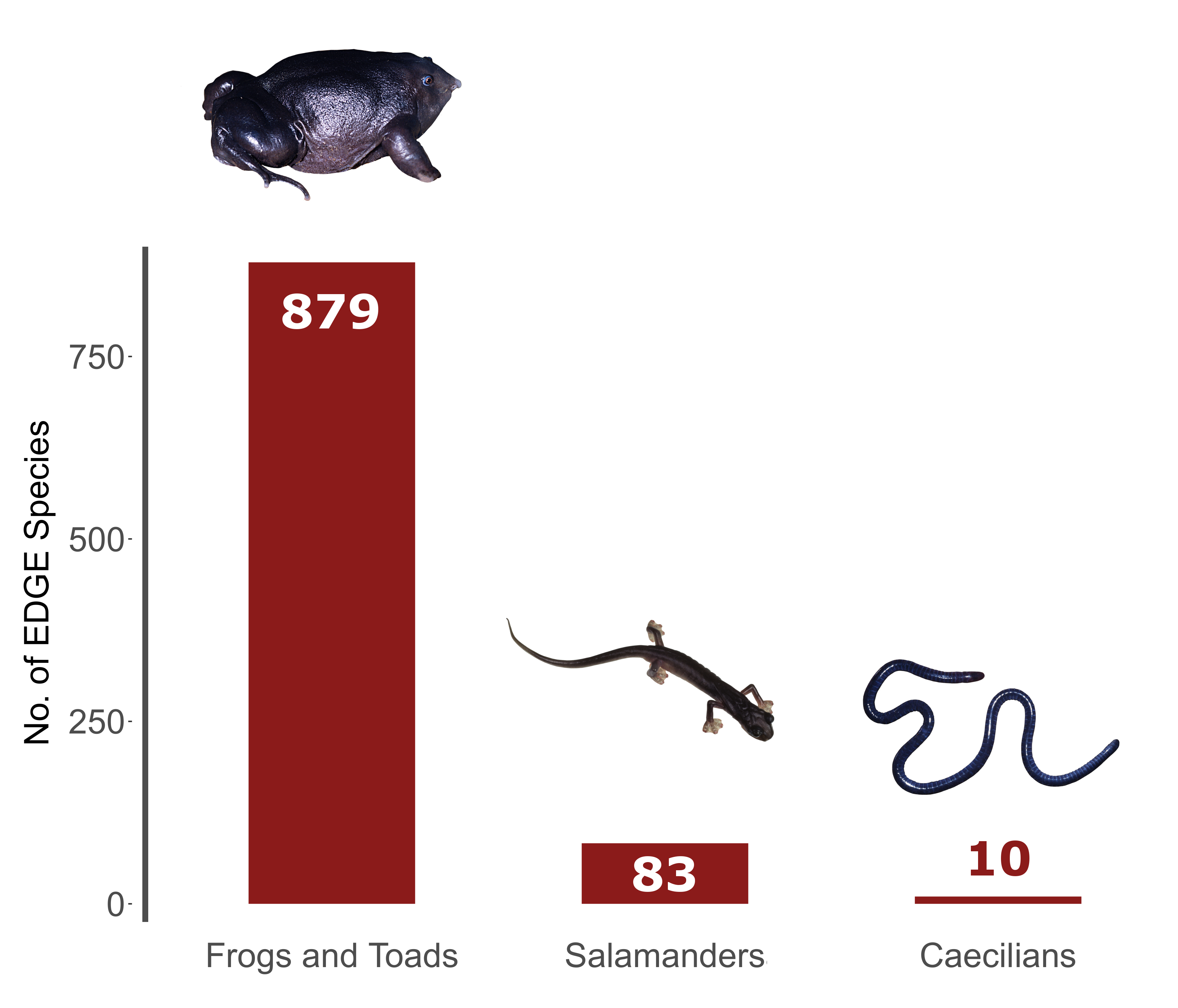
Around 30% are threatened with extinction, which is more than birds (13%) and mammals (21%). However, this is likely an underestimation of the true number, as the majority of amphibians described since 2004 have not been assessed by the IUCN Red List. At least 42% of all known amphibian species are declining, and as many as 159 amphibian species may already be extinct. There are currently 972 EDGE amphibians, which is more than any other EDGE group. Most of these are frogs and toads, due to the sheer number of species, but there are also priority EDGE salamanders and caecilians.
Click here to explore the Top 100 EDGE amphibians.
Click here for the latest EDGE Amphibians List.
When creating our EDGE amphibians list, we follow the taxonomy of Frost’s Amphibian Species of the World.
Use OneZoom to explore the tree of life!