About
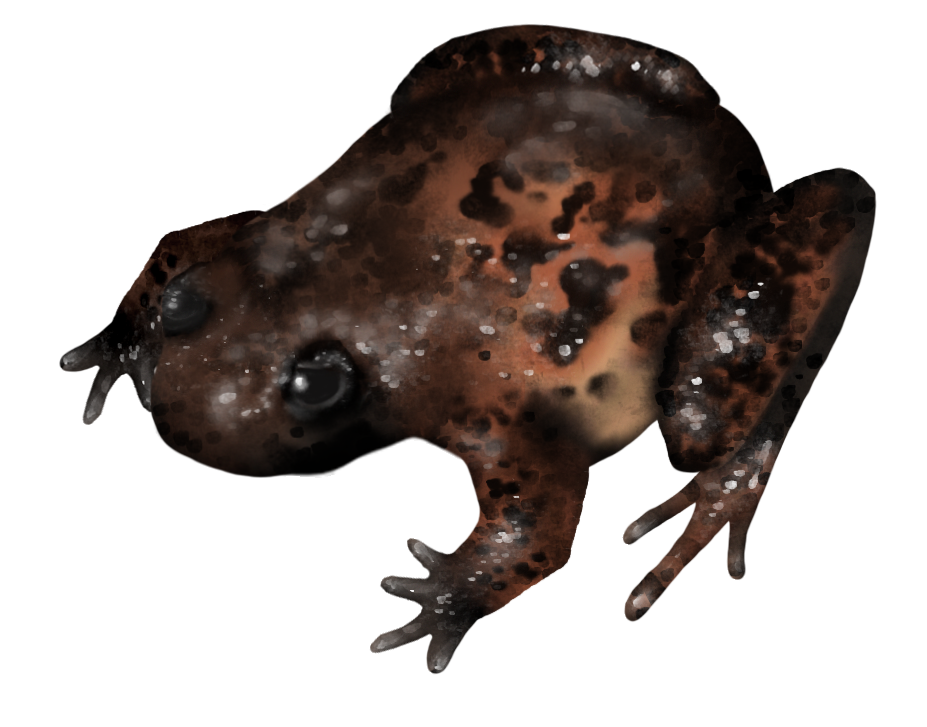
This Critically Endangered frog is one of around 15 species collectively known as “egg frogs”, and can be found in the Bamenda Highlands of western Cameroon.
The egg frog genus Leptodactylodon diverged from all other amphibians about 70 million years ago, during the Late Cretaceous. This was around 5 million years before the extinction of the dinosaurs, making them as closely-related to other frogs as camels are to whales!
Listed as Critically Endangered because its total range is estimated to be 74 km², the Bamboutos Egg Frog is known from only one location and the quality and extent of its habitat in the Bamboutos Mountains is declining continuously. The major threats to the survival of this species include the destruction and degradation of its preferred habitat by advanced deforestation, the ongoing encroachment of human settlements, and agricultural expansion.
As it is a high-elevation species, these activities may push it to the extreme part of its range and it may be susceptible to microhabitat changes caused by climate change. Unfortunately this species is not known from any protected areas and habitat protection is urgently needed in the Bamboutos Mountains.
- Order: Anura
- Family: Arthroleptidae
- Population: Common
- Trend: unknown
EDGE Score
Distribution
This species was described from the Bamboutos Mountains in the Bamenda Highlands of western Cameroon, between the altitudes of 2,300-2,700 metres above sea level. It is believed to live in a range of 74km². Despite ongoing surveys at Mount Oku, the species still has not been found there.
Habitat and Ecology
The species lives in bamboo forests and in the rainy season, grazed montane grasslands where it hides under rocks in seepage areas. It lives in drier areas than other members of its genus. It likely to breed in rocky areas in and around small streams.